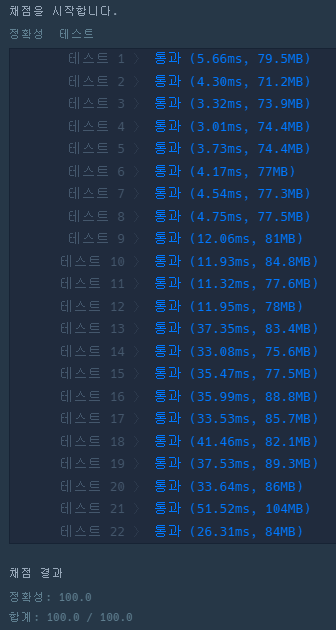
프로그래머스 Lv 3. 표 병합
Intro
공부하고 글(링크)로 남겼던 Union Find 문제를 찾아서 풀어봤습니다. 네이버에서 Union Find 검색한 후 눈에 보이는 문제 중 그나마 자주 사용해본 프로그래머스 문제를 선택했습니다.
2023 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT 문제였고, 공식 해설(링크)에서는 테스트 케이스 크기가 작아서 굳이 특별한 자료구조 사용할 필요가 없다고 합니다.
개인적으로는 테스트 케이스가 빡세지 않으니, Union Find를 간단하게 적용해보기 좋은 문제인 것 같습니다.
어떻게 풀었는지 코드와 함께 간단히 설명을 작성해 보겠습니다.
문제 정보
- 제목: 표 병합(링크)
- 난이도: 3/5
- 요약 설명
- “UPDATE r c value”, “UPDATE value1 value2”, “MERGE r1 c1 r2 c2”, “UNMERGE r c”, “PRINT r c” 와 같은 명령어를 배열로 받아, 조건에 맞게 표에 대한 명령어를 처리하는 문제
- 예제 입/출력
| commands | result |
|---|---|
| [“UPDATE 1 1 menu”, “UPDATE 1 2 category”, “UPDATE 2 1 bibimbap”, “UPDATE 2 2 korean”, “UPDATE 2 3 rice”, “UPDATE 3 1 ramyeon”, “UPDATE 3 2 korean”, “UPDATE 3 3 noodle”, “UPDATE 3 4 instant”, “UPDATE 4 1 pasta”, “UPDATE 4 2 italian”, “UPDATE 4 3 noodle”, “MERGE 1 2 1 3”, “MERGE 1 3 1 4”, “UPDATE korean hansik”, “UPDATE 1 3 group”, “UNMERGE 1 4”, “PRINT 1 3”, “PRINT 1 4”] | [“EMPTY”, “group”] |
자세한 설명은 문제를 참고해주세요.
코드
먼저 제출한 코드부터 전체적으로 보여드리고, 코드에 대해 설명하겠습니다.
전체 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private static final int SIZE = 50;
public String[] solution(String[] commands) {
List<String> answer = new ArrayList<>();
var table = new Table<String>(new String[SIZE+1][SIZE+1], new QuickFind(SIZE*SIZE));
for (var command : commands) {
String[] splittedCommand = command.split("\\s");
int r = 0;
int c = 0;
if (!(splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE") && splittedCommand.length == 3)) {
r = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[1]);
c = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[2]);
}
if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE")) {
if (splittedCommand.length == 3) {
table.update(splittedCommand[1], splittedCommand[2]);
} else {
table.update(r, c, splittedCommand[3]);
}
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("MERGE")){
int r2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[3]);
int c2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[4]);
table.merge(r, c, r2, c2);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UNMERGE")) {
table.unmerge(r, c);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("PRINT")) {
String data = table.getData(r, c);
answer.add(data == null ? "EMPTY" : data);
}
}
return answer.stream().map(String::valueOf).toArray(String[]::new);
}
class Table<T> {
private final T[][] data;
private final UnionFind unionFind;
public Table(T[][] data, UnionFind unionFind) {
this.data = data;
this.unionFind = unionFind;
}
public void update(T targetValue, T updateValue) {
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < data.length; ++j) {
if (data[i][j] != null && data[i][j].equals(targetValue))
data[i][j] = updateValue;
}
}
}
public void update(int r, int c, T value) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
updateMergedData(root, value);
}
public void merge(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
int cellValue1 = calculateCellValue(r1, c1);
int root1 = unionFind.find(cellValue1);
int cellValue2 = calculateCellValue(r2, c2);
int root2 = unionFind.find(cellValue2);
if ((r1 == r2 && c1 == c2) || root1 == root2)
return;
unionFind.union(cellValue1, cellValue2);
T updateData = null;
if (data[r1][c1] != null) {
updateData = data[r1][c1];
} else {
updateData = data[r2][c2];
}
updateMergedData(root2, updateData);
}
public void unmerge(int r, int c) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
T dataValue = data[r][c];
updateMergedData(root, null);
data[r][c] = dataValue;
unionFind.deleteAll(root);
}
private int calculateCellValue(int r, int c) {
return ((r-1) * (data.length-1)) + (c-1);
}
private void updateMergedData(int root, T value) {
List<Integer> nodes = unionFind.getConnectedComponent(root);
for (var node : nodes) {
int row = calculateRow(node);
int col = calculateCol(node);
data[row][col] = value;
}
}
private int calculateRow(int value) {
return value / (data.length-1) + 1;
}
private int calculateCol(int value) {
return value % (data.length-1) + 1;
}
public T getData(int r, int c) {
return data[r][c];
}
}
interface UnionFind {
void union(int p, int q);
int find(int p);
List<Integer> getConnectedComponent(int root);
void deleteAll(int p);
}
class QuickFind implements UnionFind {
private int[] parents;
public QuickFind(int tableSize) {
parents = new int[tableSize];
for (int i = 0; i < tableSize; ++i)
parents[i] = i;
}
@Override
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pParent = parents[p];
int qParent = parents[q];
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == pParent)
parents[i] = qParent;
}
}
@Override
public int find(int p) {
return parents[p];
}
@Override
public List<Integer> getConnectedComponent(int root) {
List<Integer> connectedComponent = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == root)
connectedComponent.add(i);
}
return connectedComponent;
}
@Override
public void deleteAll(int root) {
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == root)
parents[i] = i;
}
}
}
}
solution method
Solution 클래스의 필드와 함께, solution 메서드를 살펴보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
private static final int SIZE = 50;
public String[] solution(String[] commands) {
List<String> answer = new ArrayList<>();
var table = new Table<String>(new String[SIZE+1][SIZE+1], new QuickFind(SIZE*SIZE));
for (var command : commands) {
String[] splittedCommand = command.split("\\s");
int r = 0;
int c = 0;
if (!(splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE") && splittedCommand.length == 3)) {
r = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[1]);
c = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[2]);
}
if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE")) {
if (splittedCommand.length == 3) {
table.update(splittedCommand[1], splittedCommand[2]);
} else {
table.update(r, c, splittedCommand[3]);
}
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("MERGE")){
int r2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[3]);
int c2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[4]);
table.merge(r, c, r2, c2);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UNMERGE")) {
table.unmerge(r, c);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("PRINT")) {
String data = table.getData(r, c);
answer.add(data == null ? "EMPTY" : data);
}
}
return answer.stream().map(String::valueOf).toArray(String[]::new);
}
문제에서는 데이터 크기가 고정되어 있기는 하지만, 나름 소소하게 확장성을 생각하며 수정 편의를 위해 static 변수로 SIZE를 만들었습니다.
1
private static final int SIZE = 50;
다음으로 PRINT 명령이 나올때 마다 반환할 값을 추가해야 하는데, PRINT 명령이 몇개가 나올지는 알 수 없으므로 ArrayList를 사용하여 저장합니다.
1
List<String> answer = new ArrayList<>();
다음은 명령에 따른 테이블의 데이터 변경을 위해서 별도의 Table 클래스를 추가했습니다. 그리고 아래 Table 생성자의 두 번째 인수에 보이는 것과 같이 효율이 안좋은 QuickFind 알고리즘을 사용했는데, 뒤에가서 이야기 하겠습니다.
입력데이터가 1부터 시작하다보니 편의를 위해 데이터를 저장할 배열은 SIZE보다 1 크게 만들었고, QuickFind 알고리즘 사용시에는 parents 정보를 1차원 배열로 만들어, SIZE를 제곱한 값을 사용하게 하였습니다.
1
var table = new Table<String>(new String[SIZE+1][SIZE+1], new QuickFind(SIZE*SIZE));
다음은 아래 명령들을 처리하기 위한 코드입니다.
“UPDATE r c value”, “UPDATE value1 value2”, “MERGE r1 c1 r2 c2”, “UNMERGE r c”, “PRINT r c”
별도의 클래스를 만들어 깔끔하게 처리하기에는 시간이 부족해서 간단히 구현하였습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
for (var command : commands) {
String[] splittedCommand = command.split("\\s");
int r = 0;
int c = 0;
if (!(splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE") && splittedCommand.length == 3)) {
r = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[1]);
c = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[2]);
}
if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UPDATE")) {
if (splittedCommand.length == 3) {
table.update(splittedCommand[1], splittedCommand[2]);
} else {
table.update(r, c, splittedCommand[3]);
}
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("MERGE")){
int r2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[3]);
int c2 = Integer.parseInt(splittedCommand[4]);
table.merge(r, c, r2, c2);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("UNMERGE")) {
table.unmerge(r, c);
} else if (splittedCommand[0].equals("PRINT")) {
String data = table.getData(r, c);
answer.add(data == null ? "EMPTY" : data);
}
}
Table class
문제 푸는데는 전혀 상관 없기는 하지만, Table 클래스에서는 확장성을 생각하며 Generic을 사용하여 다른 데이터 타입의 데이터를 저장하는 것을 고려해봤습니다.
그리고 UnionFind 인터페이스를 의존하게 하여, 알고리즘을 교체할 수 있게 했습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
class Table<T> {
private final T[][] data;
private final UnionFind unionFind;
public Table(T[][] data, UnionFind unionFind) {
this.data = data;
this.unionFind = unionFind;
}
public void update(T targetValue, T updateValue) {
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < data.length; ++j) {
if (data[i][j] != null && data[i][j].equals(targetValue))
data[i][j] = updateValue;
}
}
}
public void update(int r, int c, T value) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
updateMergedData(root, value);
}
public void merge(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
int cellValue1 = calculateCellValue(r1, c1);
int root1 = unionFind.find(cellValue1);
int cellValue2 = calculateCellValue(r2, c2);
int root2 = unionFind.find(cellValue2);
if ((r1 == r2 && c1 == c2) || root1 == root2)
return;
unionFind.union(cellValue1, cellValue2);
T updateData = null;
if (data[r1][c1] != null) {
updateData = data[r1][c1];
} else {
updateData = data[r2][c2];
}
updateMergedData(root2, updateData);
}
public void unmerge(int r, int c) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
T dataValue = data[r][c];
updateMergedData(root, null);
data[r][c] = dataValue;
unionFind.deleteAll(root);
}
private int calculateCellValue(int r, int c) {
return ((r-1) * (data.length-1)) + (c-1);
}
private void updateMergedData(int root, T value) {
List<Integer> nodes = unionFind.getConnectedComponent(root);
for (var node : nodes) {
int row = calculateRow(node);
int col = calculateCol(node);
data[row][col] = value;
}
}
private int calculateRow(int value) {
return value / (data.length-1) + 1;
}
private int calculateCol(int value) {
return value % (data.length-1) + 1;
}
public T getData(int r, int c) {
return data[r][c];
}
}
메서드를 하나씩 살펴보겠습니다.
첫번째 update method
update 메서드 중 하나는 targetValue 값을 갖고 있는 경우 updateValue로 변경하는 메서드입니다. 전체 순회를 하여 비효율적입니다. 개선한다면 HashMap을 이용해서 값을 key로 하고, 행과 열 정보를 value로 하여 순회 횟수를 줄여볼 수 있겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void update(T targetValue, T updateValue) {
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < data.length; ++j) {
if (data[i][j] != null && data[i][j].equals(targetValue))
data[i][j] = updateValue;
}
}
}
순회를 유지하면서 간단하게 개선해 본다면, 아래와 같이 불필요한 null 체크는 없애볼 수 있습니다. 코드 작성할 때 null 값이 들어오지 않는 targetValue에서 equals 메서드를 사용할 생각을 못했던 것 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void update(T targetValue, T updateValue) {
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j < data.length; ++j) {
if (targetValue.equals(data[i][j]))
data[i][j] = updateValue;
}
}
}
두번째 update method
UPDATE 명령이 두 종류가 있어, Overloading을 통해 구현하였습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
public void update(int r, int c, T value) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
updateMergedData(root, value);
}
아래 그림과 같이 2차원 배열의 각 셀에 번호를 배정해두었다고 가정하고, QuickFind를 수행하는 클래스에 1차원 배열로 저장해 두었기 때문에 caculateCellValue를 이용하여 행/열 값과 Cell 값 사이의 변환이 필요합니다.
각 cell 값은 순차 증가하는 번호이므로 각 행과 열의 번호 그리고 데이터 길이를 이용하여 계산할 수 있습니다.
cell 값 = (행 번호 - 1) x 데이터 길이 + (열 번호 - 1)
코드 작성 시에는 Table 클래스의 2차원 배열 크기를 1씩 늘려줬으므로 데이터 길이에서 1을 빼주었습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private int calculateCellValue(int r, int c) {
return ((r-1) * (data.length-1)) + (c-1);
}
private int calculateRow(int value) {
return value / (data.length-1) + 1;
}
private int calculateCol(int value) {
return value % (data.length-1) + 1;
}
calculateRow, calculateCol메서드로 cell 값에서 다시 행과 열의 번호로 변환이 가능하며, 아래와 같이 ConnectedComponent 내에 있는 node의 위치를 찾아 값을 업데이트 하는데 사용하였습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
private void updateMergedData(int root, T value) {
List<Integer> nodes = unionFind.getConnectedComponent(root);
for (var node : nodes) {
int row = calculateRow(node);
int col = calculateCol(node);
data[row][col] = value;
}
}
UnionFind 를 구현할 때는 계산하는게 쉽다고 생각해서, 부모 노드 정보가 담긴 parents 배열을 1차원 배열로 만들어서 이렇게 계산이 필요하게 되었습니다. parents 배열을 2차원 배열로 만들어 부모 좌표를 저장하고, getConnectedComponent 메서드에서 각 cell의 2차원 배열 좌표 리스트를 반환했으면 더 간단해졌을텐데, 생각이 짧았습니다.
merge, unmerge, getData
호출되는 private 메서드들은 update 메서드에서 설명했고, 조건에 맞춰서 구현한 내용이라 특별히 설명할 로직은 없습니다. 시간이 부족해서 구현하지는 않았지만, r과 c는 코드가 너무 지저분해져서 위치 정보를 별도 클래스로 만들어보고 싶기는 했습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public void merge(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
int cellValue1 = calculateCellValue(r1, c1);
int root1 = unionFind.find(cellValue1);
int cellValue2 = calculateCellValue(r2, c2);
int root2 = unionFind.find(cellValue2);
if ((r1 == r2 && c1 == c2) || root1 == root2)
return;
unionFind.union(cellValue1, cellValue2);
T updateData = null;
if (data[r1][c1] != null) {
updateData = data[r1][c1];
} else {
updateData = data[r2][c2];
}
updateMergedData(root2, updateData);
}
public void unmerge(int r, int c) {
int cellValue = calculateCellValue(r, c);
int root = unionFind.find(cellValue);
T dataValue = data[r][c];
updateMergedData(root, null);
data[r][c] = dataValue;
unionFind.deleteAll(root);
}
핵심은 QuickFind 구현 로직이다보니 특별히 더 설명할게 없는 것 같습니다.
UnionFind Interface, QuickFind class
앞에서는 의도적으로 처음부터 UnionFind 인터페이스를 만든 것처럼 이야기했습니다. 그런데 사실 처음에 WQUPC(Weighted Quick Union with Path Compression)으로 구현했다가 트리 순회하는 것까지 구현하려면 시간이 너무 오래걸릴 것 같아 Quick Find로 전환하면서, 혹시 몰라 WQUPC를 살려두기 위해 인터페이스를 만들었습니다.
만약 테스트 케이스가 굉장히커서 시간제한을 통과하기 어려웠다면, WQUPC로 구현할 수 밖에 없지 않았을까 싶습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
interface UnionFind {
void union(int p, int q);
int find(int p);
List<Integer> getConnectedComponent(int root);
void deleteAll(int p);
}
class QuickFind implements UnionFind {
private int[] parents;
public QuickFind(int tableSize) {
parents = new int[tableSize];
for (int i = 0; i < tableSize; ++i)
parents[i] = i;
}
@Override
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pParent = parents[p];
int qParent = parents[q];
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == pParent)
parents[i] = qParent;
}
}
@Override
public int find(int p) {
return parents[p];
}
@Override
public List<Integer> getConnectedComponent(int root) {
List<Integer> connectedComponent = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == root)
connectedComponent.add(i);
}
return connectedComponent;
}
@Override
public void deleteAll(int root) {
for (int i = 0; i < parents.length; ++i) {
if (parents[i] == root)
parents[i] = i;
}
}
}
union과 find 메서드는 수업 시간에 배운 QuickFind로직 그대로 구현을 했고, getConnectedComponent나 deleteAll은 QuickFind 답게 전체를 순회하면서 필요한 로직을 구현하였습니다.
getConnectedComponent는 어떤 노드를 인수로 받든 해당 노드가 포함된 ConnectedComponent 를 반환할 수 있도록 했어야 했는데, 이 부분을 고려하지 못… 한게 아니고 문제풀다가 생각했는데 시간에 쫓겨 그냥 넘어갔던 기억이 납니다.
deleteAll은 오해의 소지가 있어서, deleteAllEdgesInConnectedComponent 정도가 좋아보입니다.
시간이 오래걸렸던 부분
- WQUPC으로 구현했다가 다시 QuickFind로 전환하면서 시간 소모
- Table의 2차원 배열은 SIZE 에 +1을 해서 다루었는데, QuickFind의 1차원 배열인 parents 배열과 상호작용 시에는 고려하지 않아서 대혼란
Outro
문제를 풀고나니 크게 어렵게 느껴지지 않는데, 문제를 처음 마주했을때는 수업 시간에 배우지 않았던 UNMERGE를 해야해서 당황하기도 했습니다. 지금처럼 적당히 어떻게든 되게하는거야 문제없지만, 좋은 코드를 쓰고싶은데 어떻게 해야될지 몰라서 딜레이가 생기는 것 같습니다.
한 번에 완벽할 능력은 없다보니, 차근차근 발전해 나가는 수밖에 없겠습니다. (그런데 내일 코테 예정…)
뭔가 개선할 점과 개선 방법을 찾아내고 싶은데, 블로그나 프로그래머스에 올라온 답안 중에는 참고할만한게 잘 안보이고, 코딩테스트 스터디를 해야할 때가 된 것 같습니다.